While planned maintenance and scheduled maintenance sound like the same thing, some essential differences exist between them. Simply put, planned maintenance details how and what work will be completed; scheduled maintenance determines who will complete the work and when it will be completed.
Planned maintenance starts with a problem and identifies the materials, tools, and tasks necessary to work on the problem. The planning process involves inspections, part ordering, process descriptions, and work prioritization. These responsibilities fall on the maintenance planner’s shoulders. The planned maintenance program for a facility may include scheduling, but sometimes scheduling occurs separately via a maintenance scheduler.
Scheduled maintenance begins once the work has been fully planned out. At this point in the process, the scheduler determines who will perform the work, as well as an overall timeframe for the work and a specific date to begin the work. This kind of schedule doesn’t just target specific dates—work can be performed on repeated intervals as well, like in a preventive maintenance program.
While they are different, neither planned maintenance or scheduled maintenance can exist without the other. Without maintenance planning, a job can suffer from lack of proper materials, tools, and process documentation. Without maintenance scheduling, employees may not know they are assigned to a job, the wrong employees could be assigned, and the work won’t have a clear timeline.
When both maintenance planning and scheduling operate effectively, maintenance technicians and contractors perform their work without any organizational problems.
Differences between planned and scheduled maintenance
| Planned maintenance | Scheduled maintenance | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Planned maintenance refers to the process of planning materials and tools, ordering parts, and detailing services necessary for work (how and what). | Scheduled maintenance refers to the process of setting a timeline for when maintenance work will occur, as well as assigning the proper employees to that work (who and when). |
| Workflow |  |
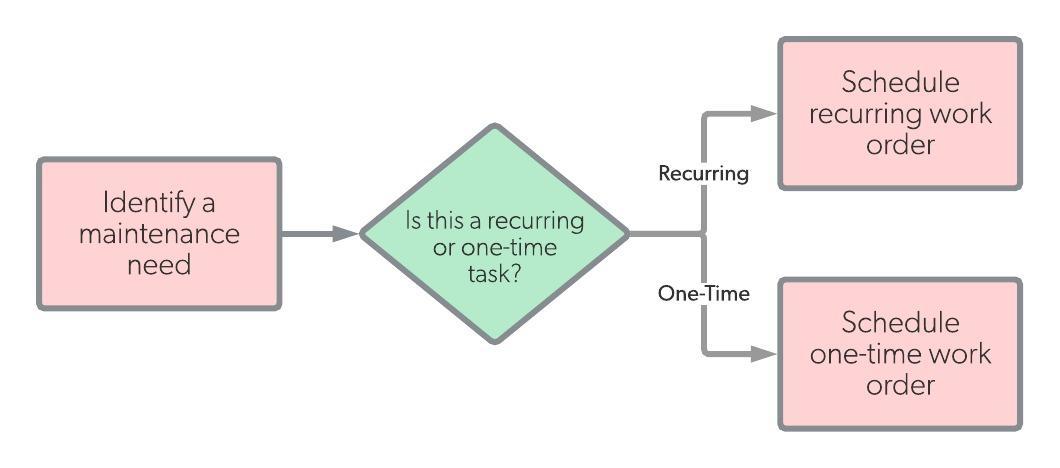 |
| Trigger | Problem identified, work order logged | Maintenance plan complete |
| Resources Needed |
|
|
| Pros |
|
|
| Cons |
|
|
| Use Case | An automotive factory uses a part that routinely applies grease to specific car parts. After a routine inspection, it’s determined that there’s extensive buildup in the machine’s output nozzle. The inspector creates a work order, which goes to the maintenance planner. The planner then maps out exactly what tools, replacement parts, and procedures need to be performed. Once the plan is complete, it’s sent to the scheduler. | Following the same example, the maintenance planner sends their plan to the scheduler. The scheduler looks over the available employees or external services, selects the necessary amount of technicians or contractors, and sets a date and time for them to perform the work. The schedule also includes information about where the issue is happening. The scheduler makes sure there are no conflicts or scheduling inconsistencies so the maintenance work occurs as planned and scheduled. |


![[Review Badge] GetApp CMMS 2022 (Dark)](https://www.datocms-assets.com/38028/1673900459-get-app-logo-dark.png?auto=compress&fm=webp&w=347)
![[Review Badge] Gartner Peer Insights (Dark)](https://www.datocms-assets.com/38028/1673900494-gartner-logo-dark.png?auto=compress&fm=webp&w=336)
