Both preventive maintenance and predictive maintenance are designed to increase the reliability of assets and reduce the amount of reactivity to failures.
With each maintenance type, work orders are scheduled well in advance of when maintenance is actually performed, making them both a form of scheduled maintenance.
The difference between preventive and predictive maintenance is preventive maintenance is regularly scheduled while predictive maintenance is scheduled based on asset conditions. Predictive maintenance reduces labor and material costs whereas preventive maintenance costs less to implement. The main difference between the two is that preventive maintenance is scheduled at regular intervals while predictive maintenance is scheduled as needed (based on asset conditions).
Because predictive maintenance is performed only when needed, it reduces labor and material costs. However, implementing a predictive maintenance program requires a substantial amount of money, training, and resources up front. These costs are often acceptable to organizations that successfully implement a preventive maintenance program.
What is Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance can be compared to an annual physical check-up. Technicians perform these maintenance tasks when everything is still running smoothly in order to prevent future breakdowns or emergency maintenance issues.
Just like a physical check-up can prevent illness or disease and lengthen your life, preventive maintenance can prevent equipment failures and extend the functional life of your assets. In addition, if you can keep your production lines up and running, you’ll be more profitable as well.
The main challenge with preventive maintenance is balancing the cost with returns. Experienced maintenance managers must make smart decisions on which machines require what preventive maintenance work and how frequently.
What is Predictive Maintenance
Although predictive maintenance is similar to preventive maintenance, this activity requires particular preset conditions. In our analogy to human health, this component can be compared with screenings or precautions recommended for an individual who is at higher risk for a particular disease due to hereditary or lifestyle considerations.
If technicians discover that a particular piece of equipment suddenly performs outside normal parameters, they trigger a predictive maintenance protocol to conveniently schedule a repair or prevent future breakdowns.
I’d highly recommend investing in a computerized maintenance management system, which will give you the measurements and data required to make smart decisions. This investment can reduce unneeded maintenance tasks, minimize maintenance costs, develop a strong overall maintenance program, and monitor the equipment and systems to keep your facility up and running.
Just as eating right, physical activity, and wellness exams all play a role in physical health, both preventive and predictive maintenance have an important place in a strategic facility maintenance program.
Differences between preventive and predictive maintenance
Because predictive maintenance is performed only when needed, it reduces labor and material costs. However, implementing a predictive maintenance program requires a substantial amount of money, training, and resources up front. These costs are often acceptable to organizations that have already successfully implemented a preventive maintenance program.
| Preventive maintenance | Predictive maintenance | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preventive maintenance (PM) is work that is scheduled based on calendar time, asset runtime, or some other period of time. | Predictive maintenance (PdM) is work that is scheduled as-needed based on real time conditions of assets. |
| Workflow | 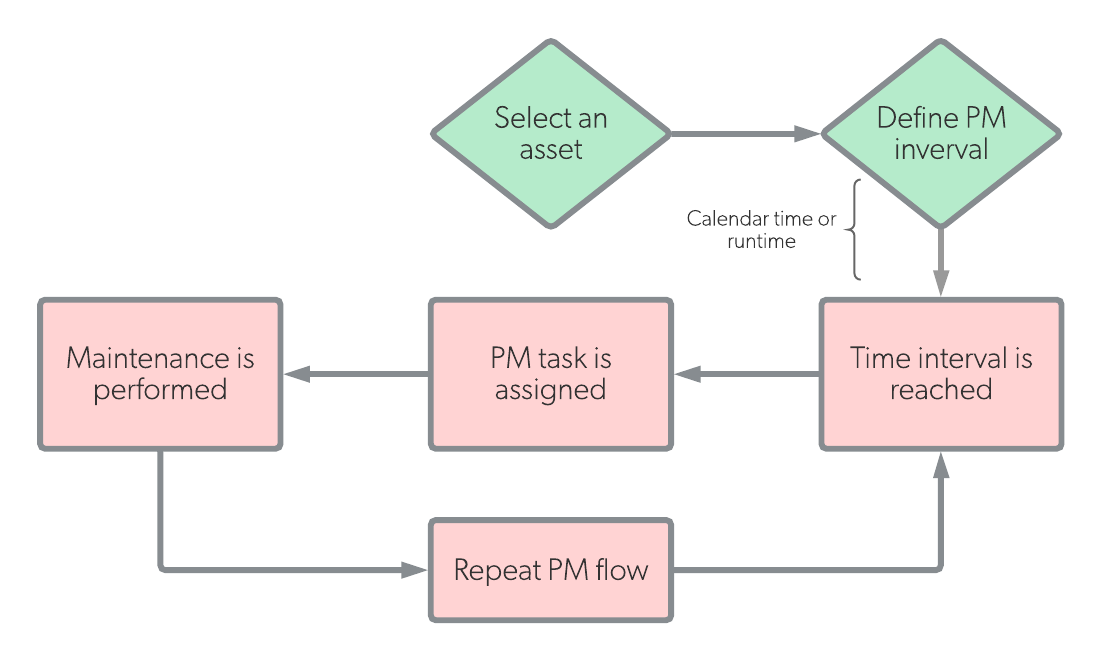 |
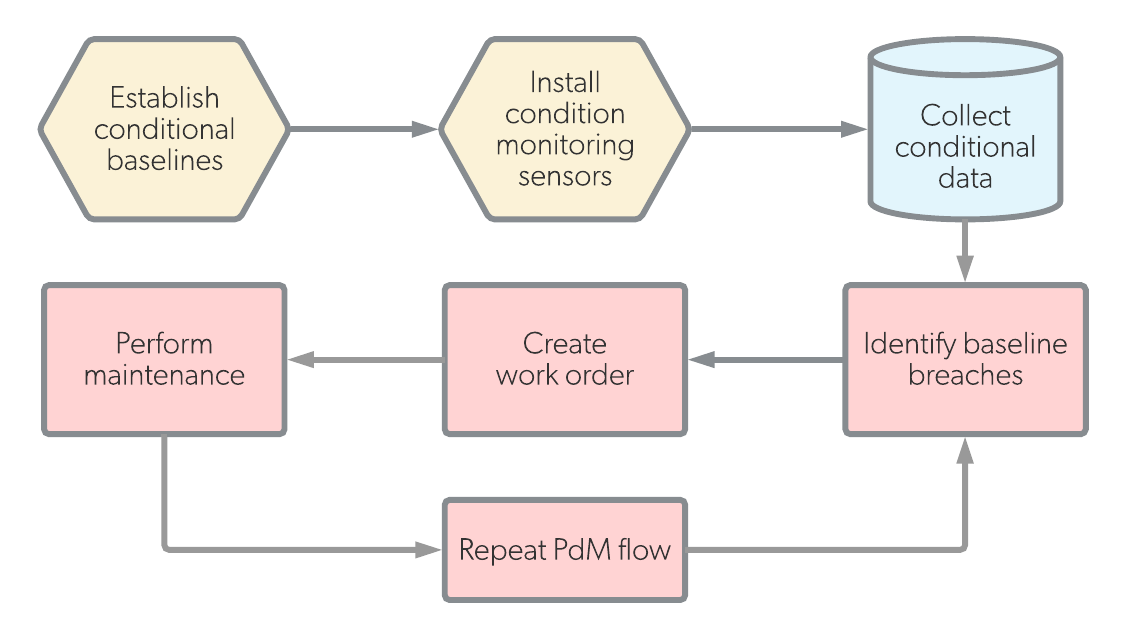 |
| Trigger | Time | Condition |
| Cost | Low | Medium/High |
| Cost Savings | 12% to 18% [1] | 25% to 30% [1] |
| Resources Needed |
|
|
| Pros |
|
|
| Cons |
|
|
| Use Case | An organization wants to decrease unplanned downtime and emergency maintenance but does not have a large maintenance budget. As a solution, they implement a PM program for select assets. Work orders are scheduled for inspections, lubrication, filter replacements, and parts replacements based on recommendations from OEMs. | An organization has assets with slow-speed bearings that frequently fail. Preventive maintenance is already in place but the organization suspects that assets are being over-greased. To perform maintenance with more precision, they use ultrasound analysis (good for slow-speed bearings). Now, work orders for greasing are only scheduled when certain ultrasound measurements are reached. |
[1] Types of Maintenance Programs by the Department of Energy, O&M Best Practices Guide, Release 3.0

![[Review Badge] Gartner Peer Insights (Dark)](https://www.datocms-assets.com/38028/1673900494-gartner-logo-dark.png?auto=compress&fm=webp&w=336)
