What is DFMEA: How To Use Design FMEA to Keep Business Safe
Design failure mode and effects analysis (DFMEA) is a process tool that helps companies locate and repair design failures. A wide variety of industries use DFMEA to help reduce overall costs of design failure. Ideally, these failures are identified early, ensuring the finished products are free from problems when they hit the market. When DFMEA is effective, you can reduce expensive consequences, such as product recalls, or even lawsuits from consumer tragedies.
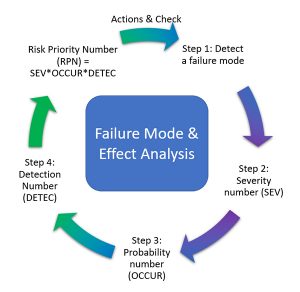
Design failure mode and effect analysis (DFMEA) helps you understand and assess potential systems, products or process failures. It's important to follow steps carefully to avoid mistakes in the process.
What is DFMEA?
DFMEA stands for design failure mode and effects analysis. Businesses use this analytical process to find and understand possible design failures.
What is the difference between DFMEA and FMEA?
FMEA, or failure mode and effects analysis, originated in the U.S. military during the 1940s. It includes a methodical process that looks at possible failures in design, production, or assembly processes, or an actual product or service. DFMEA is a component of FMEA that looks specifically at issues related to design.
Which Industries Use DFMEA?
Since DFMEA looks at possible design failure root causes, it is an effective tool for many industries. Currently, individuals who work in manufacturing, software development, healthcare, food services, and automotive industries use DFMEA.
Manufacturing
DFMEA looks at possible product malfunctions, potential safety problems, compliance issues and product life issues. Within the manufacturing industry, you can apply DFMEA to studying material properties, tolerances, and interactions between components and systems. DFMEA can help identify issues before they become costly to correct.
Software Development
Within this industry, DFMEA uses structured brainstorming to identify, rate and rank risks associated with a particular piece of software. DFMEA helps improve the quality of the software product and reduce costs associated with poor quality and software defects.
Healthcare
Medical mistakes can cause life-threatening tragedies. Any processes or procedures that can help mitigate that risk can only create improvements. DFMEA is a tool that has been embraced by several healthcare system improvement programs. These programs are focused on the design of medication systems and patient safety systems.
Food Service
DFMEA can be used effectively within the food services industry to help improve the quality and safety of a wide variety of food stuffs. In addition, the food industry is closely regulated to protect the health and safety of consumers. DFMEA can help food service organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements.
Automotive
Within the automotive industry, DFMEA provides the analytical tools that can help companies produce higher quality, safer vehicles. When customers purchase cars, they are confident that they have been designed with safety and performance in mind. DFMEA analysis can deliver on those expectations as well as help companies adhere to regulatory requirements.
The 4 Factors of the DFMEA Process
One must consider several factors when embarking on a DFMEA process. You’ll want to understand the severity of the failure, the root cause, what effects the failure has, and which mode the system was operating in when the failure occurred.
1. Severity
It’s important to develop a system to record each of these factors so you can prioritize the actions that must take place. Determining the severity of the failure looks at how serious the failure is to the overall organization. Rating or ranking each failure will bring the most serious failures to light first.
2. Cause
Determining the root cause of the failure is important in eliminating the failure in the long run. This may involve asking a series of “why” questions to find the true issue. Addressing non-root causes may offer a temporary solution, but finding the root cause is most critical.
3. Effect
You’ll also want to consider the effect that the failure has on other critical assets and your overall production line. For example, if a failure results in significant downtime, the effect of this failure will be significant. This failure would be a higher priority than one that doesn’t immediately cause negative consequences.
4. Mode
It is also important to understand the mode that your entire system was in when the failure occurred. For instance, perhaps a manufacturing failure only occurs when you are overloading the system for more than four hours. You may want to address the need to increase capacity with an additional production line.
Performing a DFMEA Audit
Depending on your industry and business, you may approach the DFMEA process in different ways. You can conduct a DFMEA audit within your organization by following these simple steps listed below.
Locate the Failed Process
Start by identifying the failed process. This may be a partial, intermittent, degraded, or unintentional failure within the system. It may result from an internal analysis of a component or system. It could also come from multiple customer complaints after a product is already released.
Assign Factors
Determine the severity, cause, effect, and mode as outlined earlier in this article. Each of these factors should be considered, rated and ranked. This data should be able to be quantitatively reviewed to help you prioritize and make smarter business decisions.
Schedule Preventive Maintenance
Once you understand the failure and the factors surrounding it, create a preventive maintenance plan to minimize this problem. This may include periodic inspections or cleaning, as well as maintenance tasks such as lubrication, calibration or tightening of components.
Locate Risk-Sensitive Processes
Evaluate your other design processes to see if there are additional risks that require mitigation. This may include components or other systems that interact or integrate with the area of failure.
Delegate Ongoing Maintenance
Management should delegate preventive maintenance duties related to these risk-sensitive processes to trained and experience team members. These process specialists should then be accountable for managing and implementing the work orders related to these areas.
4 Tips When Auditing Your DFMEA Processes
The DFMEA process can be complex, especially when you’re applying to a wide range of processes, products and assets. Here are some tips to remember when you’re going through the process.
1. Evaluate Objectively
Set up objective, reasonable criteria. If you create requirements that are either too specific or too broad, the DFMEA audit process will not be as helpful. You should they result in actions and improvements. Many criteria only focus on testing and controls.
2. Ask Experts
Communications during the process is critical to overall success. Be sure to have an ongoing dialogue with key team members. For instance, if the design failure is related to equipment in the field, be sure to consult with the maintenance technicians who work on that equipment every day during the process.
3. Stick to Schedules
Once management establishes preventive maintenance schedules, it’s important to stick to them. By implementing a CMMS solution, you can set up automated work orders that are generated according to your pre-set schedule. This tool helps increase compliance and accountability.
4. Strong Leadership
The management team that oversees the DFMEA process should be well-educated on the entire operation. Team leaders must understand the big picture so that when design failures are identified, they can make smart business decisions.
Conclusion
DFMEA is a powerful analytic tool embraced by many businesses and industries. Companies can determine the severity, cause, effect and mode of failures through this process. As a result, they can then implement preventive maintenance tasks to reduce or mitigate design problems in their overall business processes. In the long-run, this can result in safer products, a trusted reputation, and increased revenue.
Want to keep reading?
Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (DFMEA)
Failure Mode Effect Analysis Examples and Explanations
The Recommended Method of Documenting Preventive Maintenance
4,000+ COMPANIES RELY ON ASSET OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
Leading the Way to a Better Future for Maintenance and Reliability
Your asset and equipment data doesn't belong in a silo. UpKeep makes it simple to see where everything stands, all in one place. That means less guesswork and more time to focus on what matters.


![[Review Badge] GetApp CMMS 2022 (Dark)](https://www.datocms-assets.com/38028/1673900459-get-app-logo-dark.png?auto=compress&fm=webp&w=347)
![[Review Badge] Gartner Peer Insights (Dark)](https://www.datocms-assets.com/38028/1673900494-gartner-logo-dark.png?auto=compress&fm=webp&w=336)
