Proactive maintenance is a maintenance strategy that corrects the source of underlying equipment conditions. The goal of proactive maintenance is to reduce unplanned downtime, equipment failure, and risks associated with operating faulty equipment.
Proactive maintenance workflow
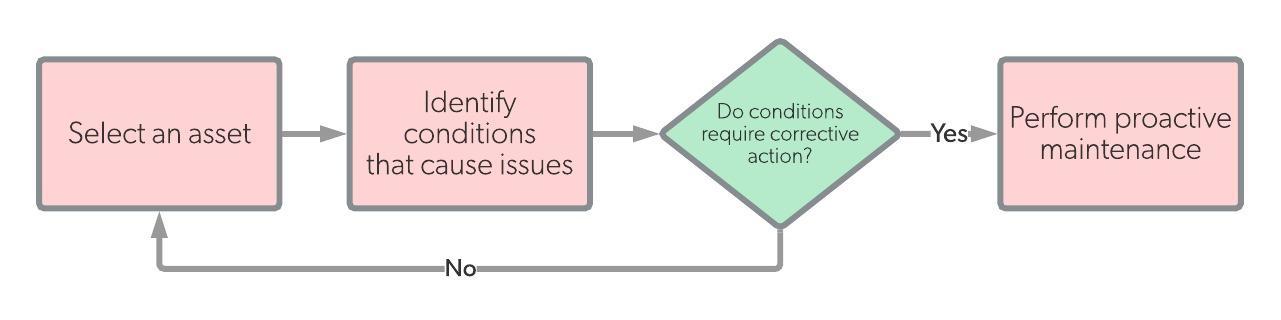
Overview
The saying “if it ain’t broke don’t fix it” seems like a practical approach to handling maintenance activities. That is until you see the huge bill for needing to urgently fix critical assets that have broken down. Unplanned downtime not only seriously impacts production but also subjects workers to safety risks from faulty equipment.
The impact of equipment reliability on the total performance of a plant has been shifting companies to more proactive maintenance philosophies. While equipment wear and tear is inevitable, investing time and resources in proactive maintenance can significantly extend the life of an asset.
In a time when technology is more advanced than ever, tools and software such as a CMMS allow for more effective and efficient implementation of proactive maintenance strategies. Proactive maintenance activities can be tracked more accurately and optimized to balance costs and risks.
Types of proactive maintenance
Proactive maintenance is any form of maintenance that is done before any significant breakdowns or failures occur. The criteria that would trigger proactive maintenance activities bring about several types of proactive maintenance.
Preventive maintenance (PM)
Preventive maintenance (PM) is one of the most common forms of proactive maintenance. In a PM program, maintenance activities are performed to keep assets in good working condition. The frequency of performing PM activities can be 1) calendar-based, 2) usage-based, 3) predictive or based on analysis of historical data, or 4) prescriptive or as determined by logical software.
Condition-based maintenance (CBM)
Other types of proactive maintenance consistently keep track of how assets perform. The frequency of tracking assets can be real-time such as in condition-based maintenance (CBM) where sensors keep close track of equipment performance to address potential issues before they happen.
Scheduled and routine maintenance
The frequency of tracking equipment performance can alternatively be manually specified. In scheduled maintenance or routine maintenance, the maintenance planner can specify schedules or routines by which equipment performance should be checked.
Proactive maintenance can take many forms, and plants would usually operate using a combination of these approaches. The most appropriate type of maintenance will depend on the type of equipment and should be carefully identified to ensure the most efficient strategy is used.
Benefits of proactive maintenance
As demonstrated by the earlier examples, proactive maintenance enables a company to reduce costs in the long run. Savings are achieved by avoiding downtime and increasing equipment reliability and availability. Equipment can also be expected to be operational for longer periods if deterioration is minimized by proactive maintenance.
An additional benefit of performing proactive maintenance is a reduced risk of safety-related incidents. Equipment, particularly that which has the possibility of catastrophic failure, would be more safely operated if a proactive maintenance approach was practiced. This is very evident in the way oil and gas companies perform stringent maintenance activities to ensure that dangerous products are contained.
The disadvantage of proactive maintenance
The benefits of proactive maintenance come with investments in time and resources. The drawback that discourages plants from shifting to proactive maintenance strategies is usually the initial costs required. Proper planning should be performed to ensure that proactive maintenance procedures are cost-effective and beneficial to the plant.
Example of proactive maintenance
Performing oil changes on a car is a relatable example of proactive maintenance. Engine deterioration from running on poor lubrication is a nightmare to fix, if even possible to fixed in the first place. What looks like a minimal investment of changing out the oil after a certain number of miles actually gives you more years on a car’s life.
To illustrate an example of proactive maintenance on a larger scale, take the case of the National Ignition Facility (NIF), the largest and most energetic facility ever built. Since 2011, a combination of maintenance activities including condition-based maintenance has enabled NIF to see projected savings of nearly $3.5 million as of 2017. Savings were attributed mostly to avoided downtime and unnecessary emergency maintenance activities.
Conclusion
Proactive maintenance refers to various strategies that can be adapted to reduce unplanned downtime and equipment failures. By properly investing resources, significant savings can be achieved through improved plant performance and safety.

![[Review Badge] Gartner Peer Insights (Dark)](https://www.datocms-assets.com/38028/1673900494-gartner-logo-dark.png?auto=compress&fm=webp&w=336)
